Learn and discover.
How to Manage RF attenuation control to Help Scale Your Wireless Lab
Wireless labs can often have many Remote Radio Units or Remote Radio Heads (RRUs/RRHs) to manage. To conduct testing, these RF ports are connected to RF attenuation equipment before being routed to RF testing stations.
Network Slicing brings revenue opportunities and testing challenges for operators
Mobile carriers have invested considerably in deploying 5G New Radio (NR) and 5G standalone (SA) networks. One of the most promising features of 5G Standalone (SA) to help monetize new services for subscribers is Network Slicing.

Handover Testing Made Simple
To simulate a handover, testers must precisely control RF signal strengths from two or more sites simultaneously. Techniques such as MIMO and Carrier Aggregation (CA) combine multiple RF signals together to improve network performance, but testers must manipulate many different signals simultaneously to properly simulate a single handover.


Sharing Limited Test Resources Among Multiple Testers
One of the biggest issues seen in RF labs is the need to share expensive and limited test resources among a larger group of testers. Ideally, all testers would have their own, dedicated test equipment. However, much of this equipment is very expensive so this isn’t really a practical approach in most labs.
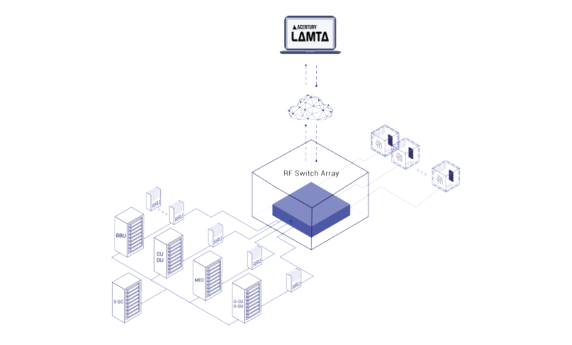
Replacing RF patch panels with a software-controlled RF switch matrix
One of the most common issues facing RF lab managers is the cost of setting up various RF testing scenarios, executing the tests, and then tearing down those same setups. Not only is this tedious, time-consuming, and manual labour, it also creates excessive stress and strain on expensive RF components.
